Phác đồ điều trị bệnh E.coli dung huyết sưng phù đầu ở lợn | VTC16
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่
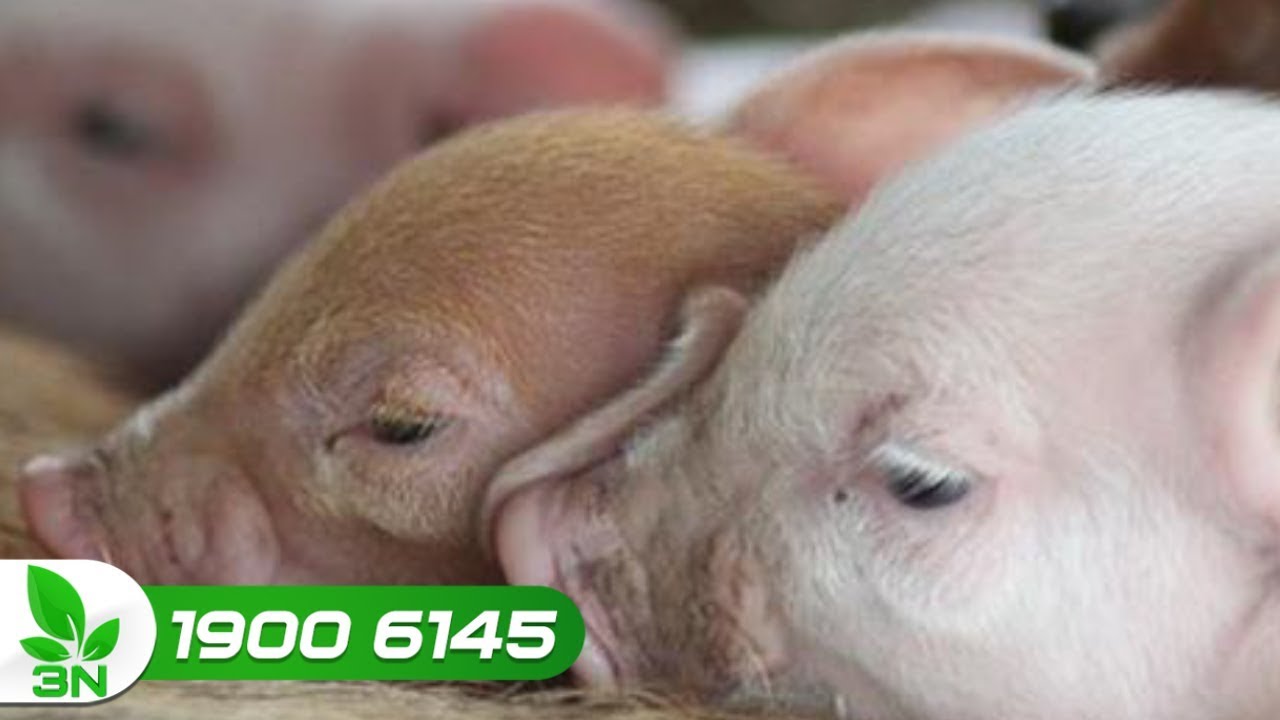
VTC16 | 1 đàn lợn con 40 ngày tuổi. Hiện tượng sưng phù đầu, hai mắt đỏ nóng sốt, há miệng thở, đi ngoài phân lỏng nhầy, xóa mùi hôi, bỏ ăn, chết nhanh, ngoài ra bình thường, bị 1 tuần, có biểu hiện lây sang đàn khác, đã dùng thuốc nhưng không hiệu quả. Hỏi nguyên nhân có phải lợn mắc bệnh do vi khuẩn E.coli dung huyết hay không? Và cách khắc phục như thế nào?
Kênh Truyền hình Nông nghiệp Nông thôn (VTC16)
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/3NTVVN
Xem lại chương trình tại Website: http://mnongnghiep.vn/
Tổng Đài: 1900.6145
Email: [email protected]
Địa chỉ: Tầng 8, Tòa nhà VTC Tower số 23 Lạc Trung, Quận Hai Bà Trưng, Thành phố Hà Nội

What is E.Coli? What can you do to protect yourself and others?
E.coli is a bacterium that is commonly found in the gut of all humans and most warmblooded animals. Most strains of E.Coli have beneficial functions. For example they may prevent harmful bacteria from establishing themselves in the intestine. There are some strains of E.Coli, however, that are pathogenic, which means that they can cause diseases.
Subtitles are available in English, French, German, Italian and Spanish. Click on the setting button to select your preferred language subtitles and then click on “turn on captions” button in the lower right hand corner of the screen.
Discover more about EFSA on our channels:
▪ Website: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en
▪ Twitter: https://twitter.com/efsa_eu
▪ LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/efsa
▪ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/efsa_eu

Gà bị bệnh E.coli ghép thương hàn, cách trị hiệu quả | VTC16
VTC16 | Đàn gà 500 con, thả vườn, được 45 ngày tuổi. Mấy ngay nay có hiện tượng ủ rũ, kém ăn, xù lông, phân trắng có nhầy, phân xáp, phân đen như luyn 1 vài con có hiện tượng diều cứng, rụng lông dưới phần cánh, gà mổ ăn thân chuối nhiều, đã làm vacxin new 2 lần đang dùng thuốc có hoạt chất ampicilin,colistin và thuốc cầu trùng được 3 ngày, bên cạnh đó có cho uống nước tỏi và nước gừng. Hỏi nguyên nhân và cách khắc phục bệnh cho gà?
Kênh Truyền hình Nông nghiệp Nông thôn (VTC16)
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/3NTVVN
Xem lại chương trình tại Website: http://mnongnghiep.vn/
Tổng Đài: 1900.6145
Email: [email protected]
Địa chỉ: Tầng 8, Tòa nhà VTC Tower số 23 Lạc Trung, Quận Hai Bà Trưng, Thành phố Hà Nội

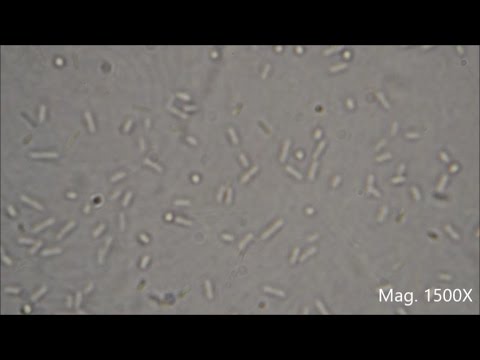
Bacteria under the Microscope (E. coli and S. aureus)
Bacteria species E. coli and S. aureus under the microscope with different magnifications. Bacteria are among the smallest, simplest and most ancient living organisms. They are found in every single environment, inside and outside of plants and animals. They are so small that a small drop of water can contain millions of bacteria cells.
While some species can make you sick, some are actually beneficial to humans and can help prevent infection, allergies, help with digestion and produce nutrients in our stomach and intestines. Some actually produce antibiotics that we can use against other bacteria!
The magnification of each shot is shown in the bottom right hand corner.
T4 Phage attacking E.coli
The WHO estimates up to 700,000 patients died in of multidrug resistant bacterial infections globally in 2016. This rise of multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria is mainly driven by the excessive use of antibiotics in meat production. Some estimates claim 80% of antibiotics produced globally are used on poultry and pigs. The health threat posed by MDR infections prompted researchers to explore phage therapy again. Several publications have recently reported spectacular successes in the fight against MDR bacterial infections in humans but also livestock. While in the past phage therapy was shunned by pharma companies for various challenges (see below), now the commercial potential and advances in genetics have enticed biotech companies to exploit the deadly potential of phagetherapy as a secret weapon to kill superbugs.
Please subscribe to our channel, if you like this content to show your support for our work. Thank you!
Now about the amazing nanoworld of bacteriophages:
More than 100 years ago the FrancoCanadian scientist Felix d’Herelle identified bacteriophages! They look like spaceships from another world and are most fearsome killing machines, fortunately they are targeting exclusively bacteria. D’Herelle and his colleague George Eliava immediately realised phages could be weaponised to help patients to fight off bacterial infections. However, in the western hemisphere the control of lifethreatening bacterial infections was soon achieved with antibiotics, while phages and viruses became favourite research tools of geneticists. This explains why the bacteriophage T4, which is depicted here, is one of the most intensely studied biological objects. However, phage therapy was pioneered by the Eliava Institute in Georgia, where it has been advanced ever since its discovery.
Phages stick to bacteria with their leglike fibres, which triggers a change in the protein conformation ramming their shaft into the bacterial hull. The interior of the shaft contains a needle, which punctures the bacterial envelope enabling the phage to inject its genetic material. The phage genome within minutes overcomes the bacterial defences, phage components are assembled within the cell before it ruptures to release a new wave of phages. Several biotech companies are now ready to exploit the deadly potential of phage therapy as a secret weapon to kill superbugs.
Phage therapy frequently relies on extensive phage collections.
One of them is maintained with the support of students searching phages, which can be found virtually everywhere. SEAPHAGES (https://seaphages.org/) is a twosemester, discoverybased undergraduate research course that begins with simple digging in the soil to find new viruses, but progresses through a variety of microbiology techniques and eventually to complex genome annotation and bioinformatic analyses. It has assembled under the supervision of Graham Hatfull’s group at the University of Pittsburgh and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science Education division a collection of more than 15.000 phages. In 2019 the Hatfull lab hit the headlines, when they reported in Nature Medicine, that geneticall engineered phages had cured a terminally ill cystic fibrosis patient, who was suffering from multidrug resistant bacterial infections in the lung: https://www.nature.com/articles/s415910190437z
Please feel free to use our images and videos for noncommercial purposes like teaching, or get in touch if you are interested in scientifically accurate animation of high quality. We appreciate if you follow our channel for more of our animations.
Music by: Ross Bugden Last Dawn (Copyright and Royalty Free)
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCQKGLOK2FqmVgVwYferltKQ
This video was produced by biolution GmbH and can be shared freely without changes for noncommercial purposes.
DNA bacteriophage research science technology teaching
References:
WHO on antimicrobial resistant bacteria: https://www.who.int/newsroom/factsheets/detail/antimicrobialresistance
The dawn of phage therapy. Sana Rehman et al. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.2041
Engineered bacteriophages for treatment of a patient with a disseminated drugresistant Mycobacterium abscessus. Rebekah M. et al. Nature Medicine volume 25, pages730–733 (2019) https://www.nature.com/articles/s415910190437z
Specific and Selective Bacteriophages in the Fight against Multidrugresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Bagińska N, et al. Virol Sin. 15. doi: 10.1007/s12250019001250.
Successful adjunctive use of bacteriophage therapy for treatment of multidrugresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a cystic fibrosis patient. Law N, et al., Infection. 2019 May 17. doi: 10.1007/s15010019013190.
Synergistic effect of phage therapy using a cocktail rather than a single phage in the control of severe colibacillosis in quails. Naghizadeh M et al., Poult Sci. 2019 Feb 1;98(2):653663. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey414.

นอกจากการดูหัวข้อนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถเข้าถึงบทวิจารณ์ดีๆ อื่นๆ อีกมากมายได้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่Sales experience